7-7 Filling and Wrapping - Concepts and Explanations
Surface Area of Rectangular Prisms
Surface area is the sum of the areas of the faces.
Surface Area = (area of the front x 2) + (area of the side x 2) + (area of the top x 2)
Or
Surface Area = (area of the front + area of the side + area of the top) X 2 = (w X h + w X l + l X h) X 2.
Example
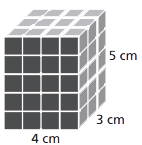
There are three sets of two congruent faces:
4 cm by 3 cm (area is 12 cm2);
4 cm by 5 cm (area is 20 cm2);
3 cm by 5 cm (area is 15 cm2).
Surface area = 94 cm2
Volume of Rectangular Prism
The volume (the total number of unit cubes) of a rectangular prism is the area of its base (the number of unit cubes in the first layer) multiplied by its height (the total number of layers).
Volume = Area of the base x height = Bh = lwh
Example

3 X 2 = 6 cubes on the base
5 layers of cubes (height);
Volume = 6 X 5 = 30 cubic units
Volume of Prisms
The same layering strategy is used to generalize the method for finding the volume of any prism. The volume of any prism is the area of its base multiplied by its height.
Volume = Area of the base X height = Bh
Example

Area of Circles
Students begin by finding the number of “radius squares” with side lengths that are equal to the radius, that cover the circle. It is a little more than 3, or pi.
Example
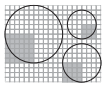
The area of a circle is pi X a "radius square" or pi X radius X radius = π X r X r
= πr2
Perimeter of Circles (Circumferences)
Students count the number of diameter lengths needed to surround the circle. It is a little more than 3, or pi.
Example
The circumference of a circle is pi X diameter, or πd.
Surface Area of Cylinders
By folding a flat pattern to form a cylinder, students discover that the surface area of the cylinder is the area of the rectangle that forms the lateral surface (2 πrh) plus the areas of the two circular ends (2πr2). Surface Area = 2πr2 + 2πrh
Example
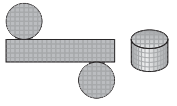
Use 3.14 for π. r = 4 h = 5.
2π x 42 + 2π x 4(5) = 100.48 + 125.6
≈ 226.08 square units.
Volume of Cylinders
The volume of a cylinder is the number of unit cubes in one layer (the area of the circular base, πr2) multiplied by the number of layers (the height h) needed to fill the cylinder. Volume = Bh = πr2h.
Example
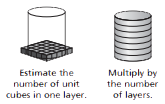
Area of base B = π r2
≈ 3.14 X 2.52
= 19.625 square units
V = Bh
= 19.625 X 7
= 137.375 cubic units
Volumes of Cones and Spheres
If a cylinder, a cone, and a sphere all have the same radius and the same height (the height being equal to two radii), then it takes 3 cones to fill the cylinder, and 1 1/2 spheres to fill the cylinder.
Volumecone = 1/3 x Volumecylinder = 1/3πr2h
Volumesphere = 2/3 x Volumecylinder = 2/3πr2h.
Example
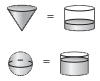 Volumecylinder = 628 cm3
Volumecylinder = 628 cm3
Volumecone ≈ 209 cm3
Volumesphere ≈ 419 cm3